Science labs are easier and more effective than ever with ExploreLearning Gizmos
ExploreLearning Gizmos library covers 550+ math and science topics with interactive simulations delivering results that matter without all the fuss. Our Top Ten Quarterly Gizmos are a specially curated list of virtual labs educators use to bring their students powerful learning experiences. Are you ready to effectively use valuable class time, foster curiosity, and impact student achievement without messy materials to prepare or post-lab cleaning?
Check out the Top Ten Quarterly Gizmos with your students.

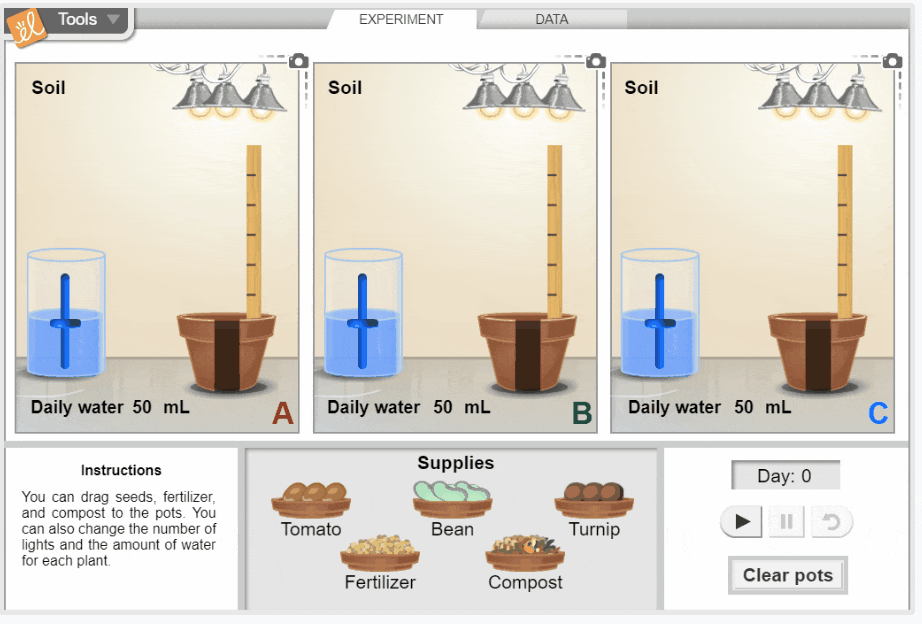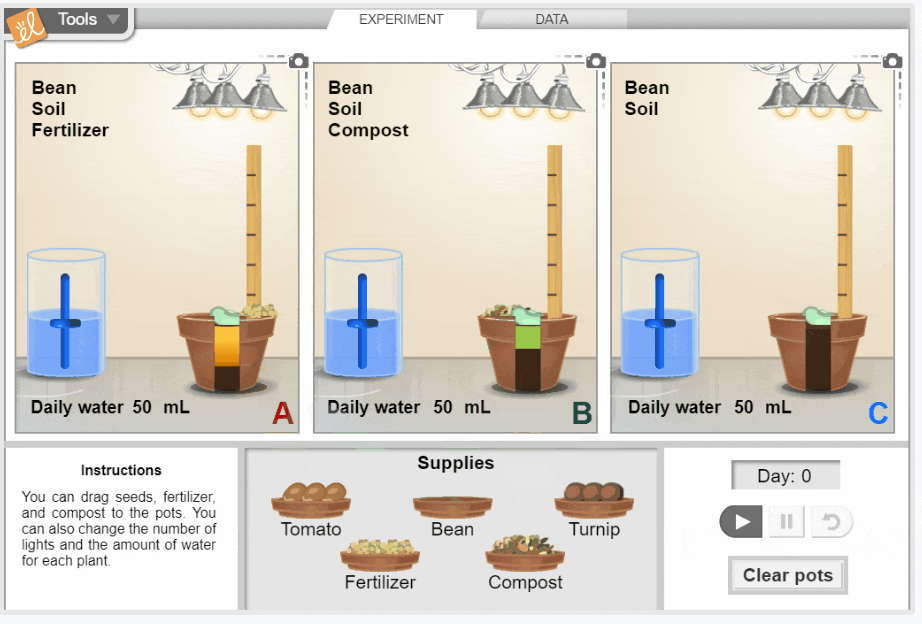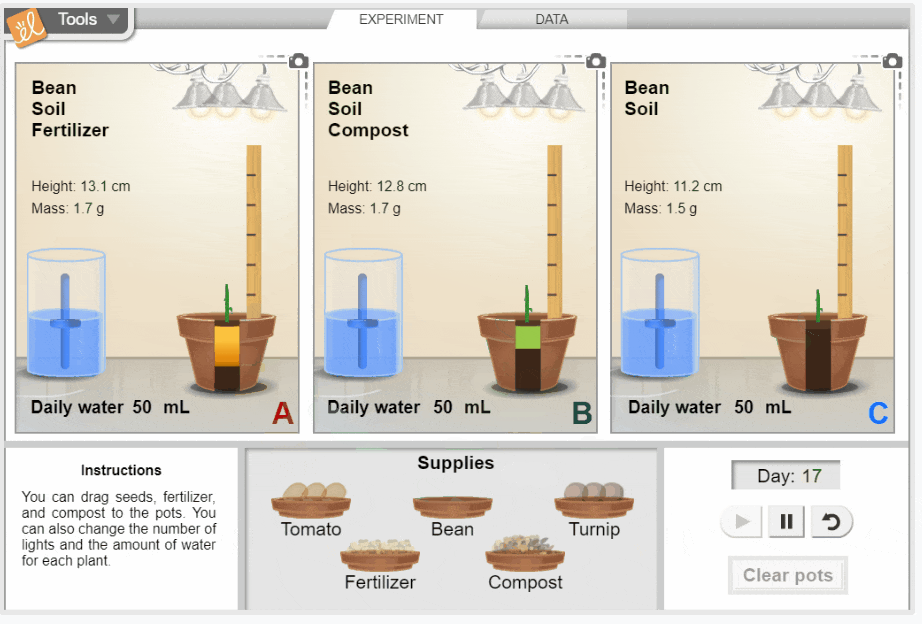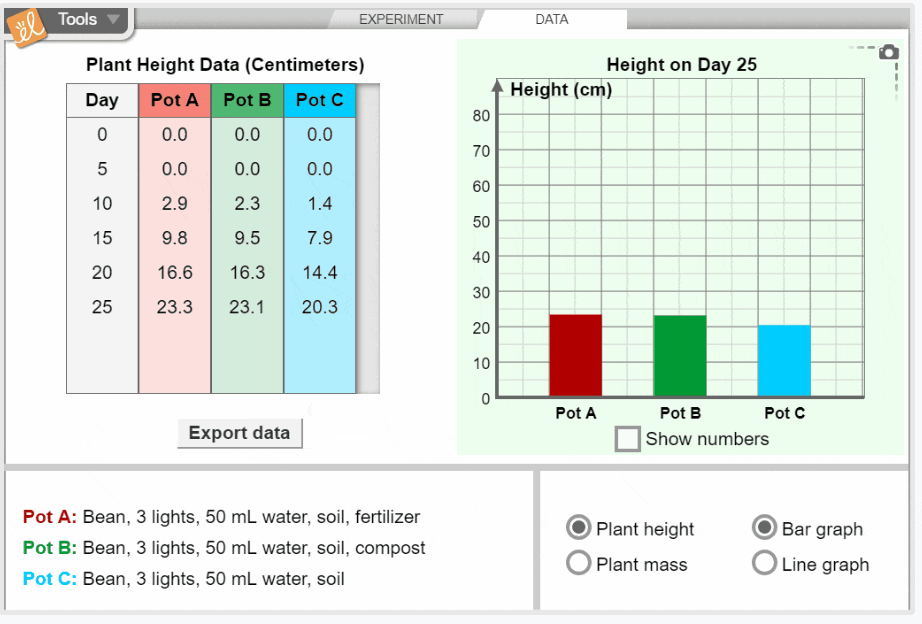
Growing Plants
Investigate the growth of three common garden plants: tomatoes, beans, and turnips. You can change the amount of light each plant gets, the amount of water added each day, and the type of soil the seed is planted in. Observe the effect of each variable on plant height, plant mass, leaf color, and leaf size. Determine what conditions produce the tallest and healthiest plants. Height and mass data are displayed on tables and graphs.
.gif)
Graphing Skills
Create a graph (bar graph, line graph, pie chart, or scatter plot) based on a given data set. Title the graph, label the axes, and choose a scale. Adjust the graph to fit the data, and then check your accuracy. The Gizmo can also be used to create a data table based on a given graph.
.gif)
Cell Structure
Select a sample cell from an animal, plant, or bacterium and view the cell under a microscope. Select each organelle on the image to learn more about its structure and function. Close-up views and animations of certain organelles are provided.
.gif)
Measuring Volume
Measure the volume of liquids and solids using beakers, graduated cylinders, overflow cups, and rulers. Water can be poured from one container to another and objects can be added to containers. A pipette can be used to transfer small amounts of water, and a magnifier can be used to observe the meniscus in a graduated cylinder. Test your volume-measurement skills in the "Practice" mode of the Gizmo.
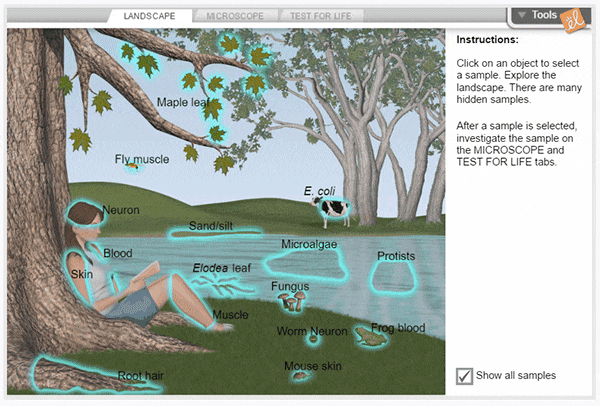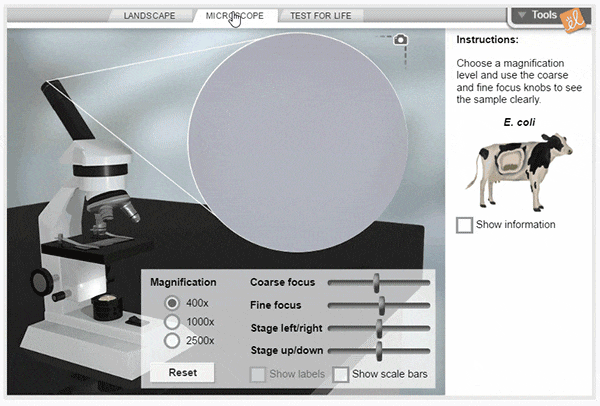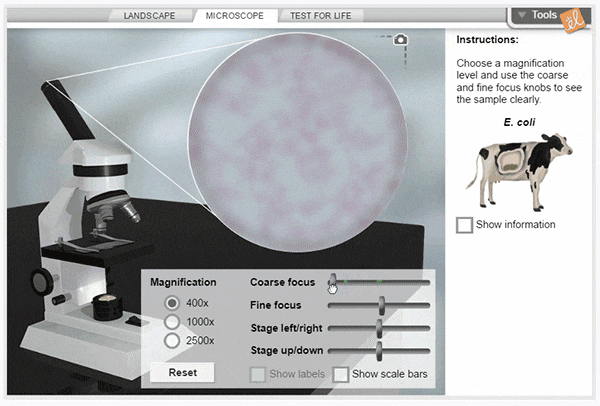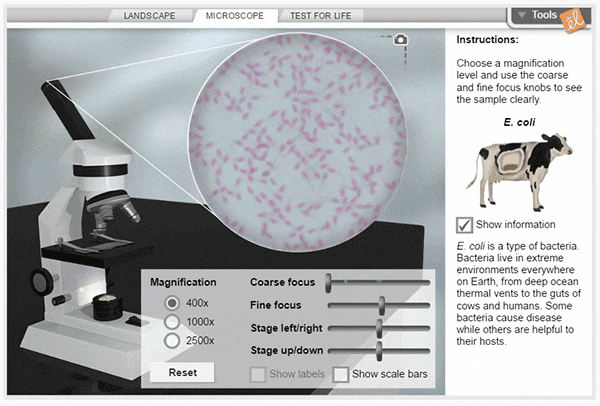
Cell Types
Using a compound light microscope, explore a wide variety of cells, from bacteria to human neurons. Select a sample to study, then focus on it using the microscope's coarse and fine focus controls. Compare the structures found in different cells, then perform tests to see if the sample is alive.

Density Laboratory
With a scale to measure mass, a graduated cylinder to measure volume, and a large beaker of liquid to observe flotation, the relationship between mass, volume, density, and flotation can be investigated. The density of the liquid in the beaker can be adjusted, and a variety of objects can be studied during the investigation.
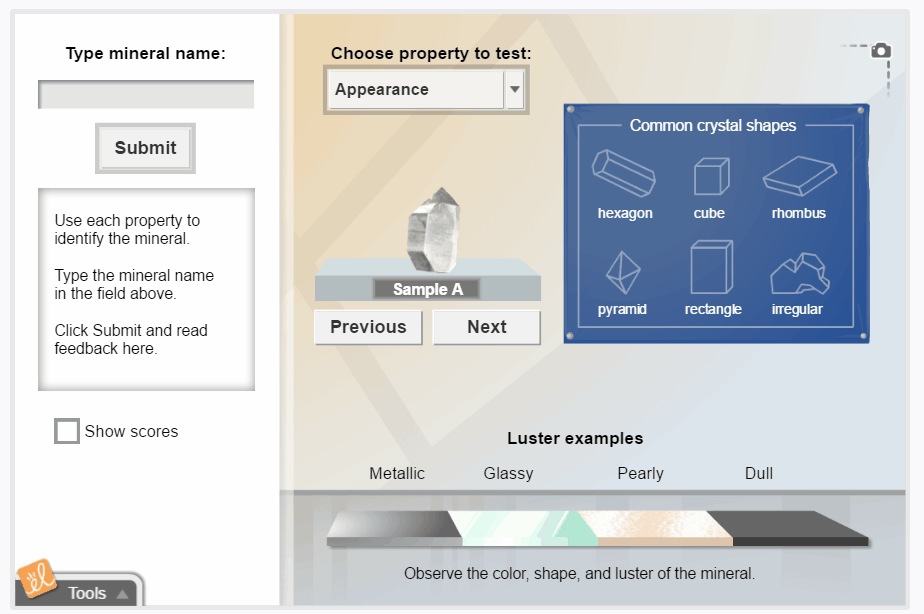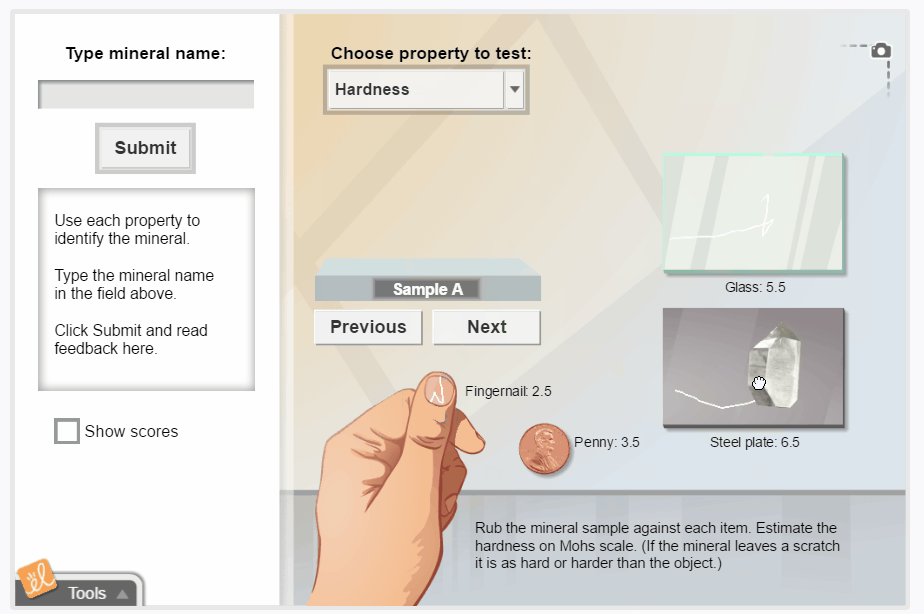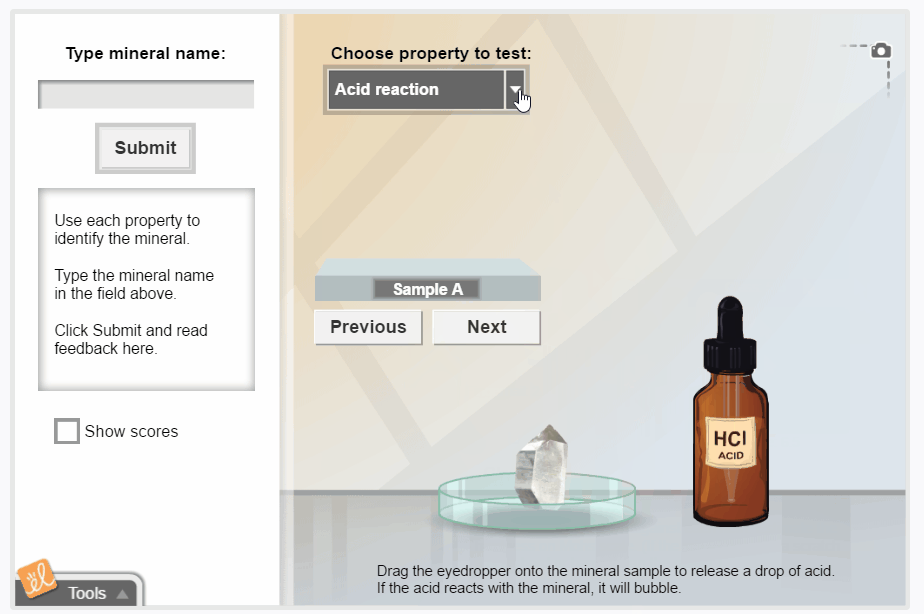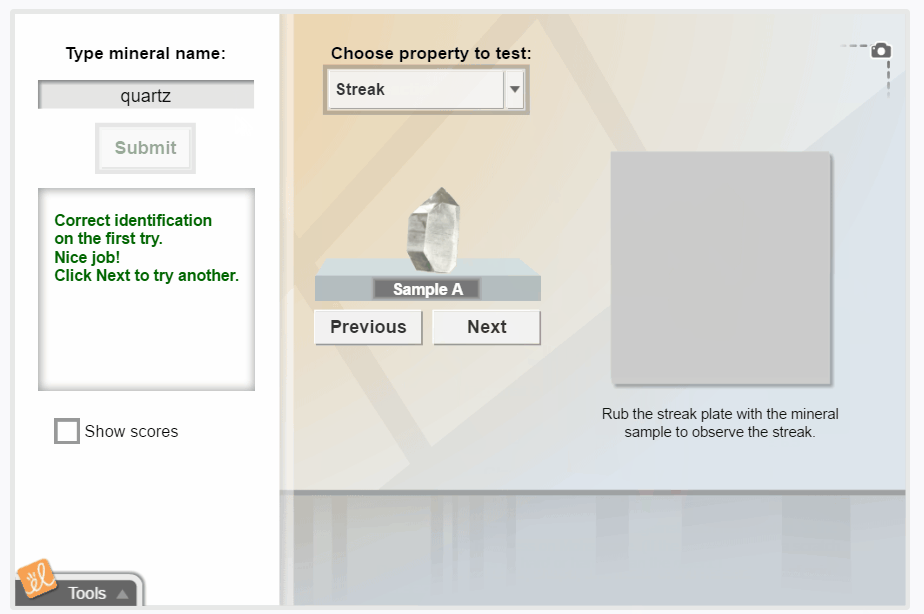
Mineral Identification
Observe and measure the properties of a mineral sample, and then use a key to identify the mineral. Students can observe the color, luster, shape, density, hardness, streak, and reaction to acid for each mineral. There are 26 mineral samples to identify.
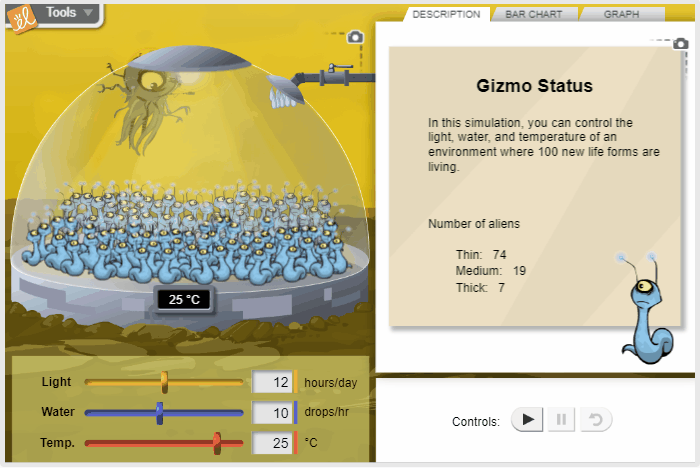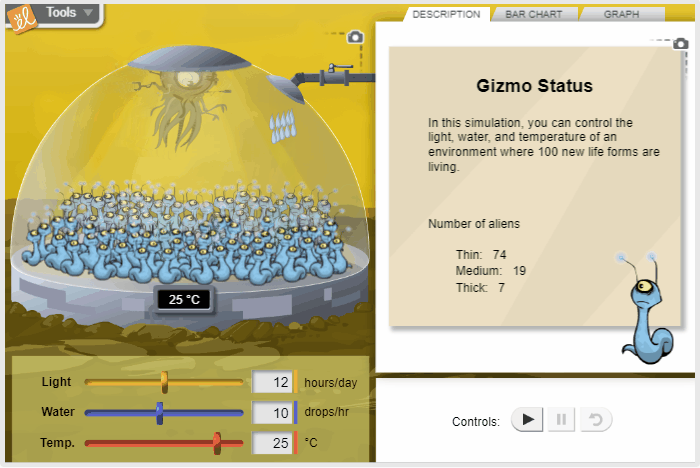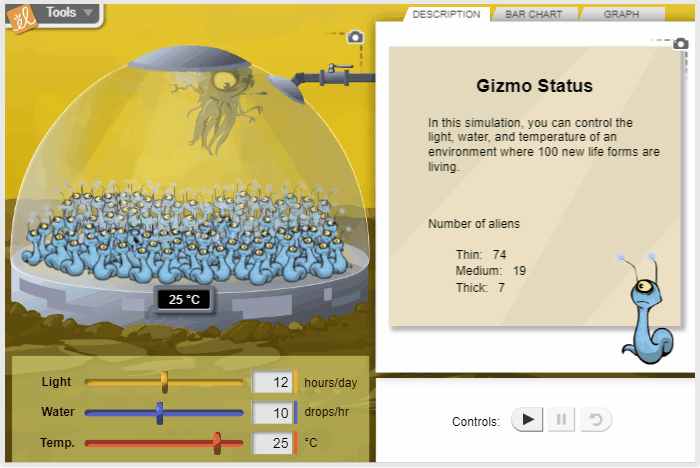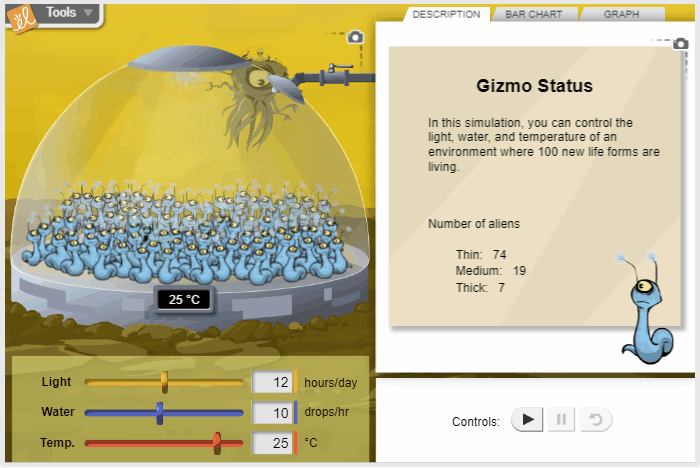
Effect of Environment on New Life Form
Using the scientific method, control the environmental conditions for a fictional alien organism in order to learn how the organism responds to changes in conditions. Sunlight, water, and temperature can be varied to determine their effects on the shape of the aliens.
.gif)
Triple Beam Balance
Learn how to determine an object's mass using a triple beam balance. This simulated version of a common real-world laboratory tool for measurement can be used to determine the mass of various objects.

Phase Changes
Explore the relationship between molecular motion, temperature, and phase changes. Compare the molecular structure of solids, liquids, and gases. Graph temperature changes as ice is melted and water is boiled. Find the effect of altitude on phase changes. The starting temperature, ice volume, altitude, and rate of heating or cooling can be adjusted.
